Announcements
- Information about the final project is now available. The next milestone, the report itself, is due 2023-12-15T23:59:00-05:00.
- Be sure you’ve familiarized yourself with the course’s syllabus, particularly its provisions concerning academic honesty, lateness, and extensions.
Gallery
Here are just some of Fall 2023’s final projects, randomly ordered.
An APT took advantage of a signing key to forge authentication tokens to steal email information from numerous organizations (e.g federal). A federal entity is the one who tipped off CISA/MS to look into it where the MS was lambasted for not having that logging feature automatically availability and had it behind another pay wall.
M0veIt's exploitation through SQL injection vulnerabilities caused great damage to my company's operation earlier this year. We see public knowledge about this attack in: CVE-2023-34362, news articles about my employer being compromised, and NIST references. I would like to take a fresh approach to examining this situation by proposing a hypothesis for the cause of so many endemic software security problems. I would like to assert that major, complex problems like these are a direct result of staffing decisions about the ratios of software engineers to business people in a software-centric commercial operation.
Title: The Capital One Data Breach Date: July 15, 2023 In July 2023, a former AWS employee exploited a vulnerability in Capital One's firewall, causing a data breach that exposed the personal information of over 100 million customers and applicants. This breach was a significant embarrassment for Capital One and raised concerns about the security of sensitive personal information stored by major corporations using cloud computing. Capital One implemented enhanced security measures, including stricter access controls and enhanced firewall configurations, in response to the breach. They also offered free identity theft protection and credit monitoring to affected customers. The breach at Capital One serves as a reminder that no organization is entirely immune to cyber attacks. Protecting data, such as using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and being cautious about the information you share online, is essential.
The threat I would like to discuss is the SQL injection vulnerability of the MOVEit file transfer application. Some reports say that the vulnerability was reported all the way back in versions from 2021, but the first exploit that resulted in a breach was first disclosed on May 31st 2023, with several hundreds more occurring between then and August 8th 2023.
I would like to discuss the thread known as TA473. More specifically, the attacker took advantage of a vulnerability on the Zimbra mail server. They used phishing, which contained URLs that led to cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. The thread was made public on March 31, 2023.
I'm going to discuss the 23andMe data breach. This was made public knowledge on October 6, and resulted in the theft of user data including genetic background, sex, birth year, and other details, targeting Ashkenazi Jews and people of Chinese descent.
The subject of my final project will be the recent LastPass breach and it's origins. The original incident was disclosed to the public on Dec. 22, 2022. However, multiple updates and revelations occurred throughout 2023.
MGM Resorts International experienced a cyberattack by the criminal group Scattered Spider, which began with a vshiing attack on September 7 and was detected on September 11 due to disruptions caused by malware. The company publicly acknowledged the incident on the same day via a statement on a platform called "X" (formerly Twitter). The attackers exploited social engineering to reset a user's multi-factor authentication and gained control of MGM's Okta and Microsoft Azure cloud services. Subsequently, the threat actors, discovered but not before exfiltrating data, encrypted over 100 ESXi servers, causing widespread disruptions to hotel operations and financial losses estimated at millions of dollars per day. The attack persisted for about 10 days, and investigations are ongoing to determine the full scope of damage and data compromise.
An Okta employee saved company login credentials to a personal Google account. The personal account was apparently compromised when a connected device was compromised, exposing the credentials. The credentials were used for unauthorized access to the Okta customer support system, accessing customer information.
The threat that I would like to discuss is a worm attack. In the recent events and ongoing war between Russia and Ukraine, Russia's cyber espionage launched a worm attack on Ukraine's organizations to maintain a watch and accumulate data from them, and this group utilized a USB worm that went beyond Ukraine and was even discovered on the US and other countries.
For my final project, I would like to propose the MGM cyberattack. In September 11, 2023, MGM Resorts announced that they were affected by ransomware which cost them $100 million. MGM lost availability to their main website, reservation systems, and in-casino services.
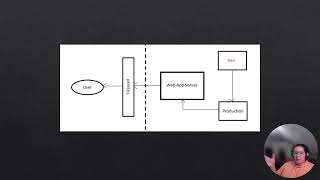
For the project, i would be discussing a Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) vulnerability. In an SSRF attack, the attacker can use server functionality to read or update internal resources. By carefully selecting the URLs, the attacker may be able to read server configuration such as AWS metadata, connect to internal services such as http enabled databases, or perform post requests towards internal services that are not intended to be exposed.
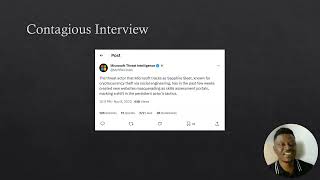
The threat I would like to discuss appears to have been made public on 11/8/2023 by Microsoft's Threat Intelligence team on the X platform (https://twitter.com/MsftSecIntel/status/1722316019920728437). It is a social engineering campaign whereby North Korean hackers created a series of websites pretending to be skills assessment portals. The hackers pretend to be job recruiters reaching out to users on LinkedIn. After a series of conversations, they move the communication offline getting IT job seekers to register for these skills assessment portals. This allows the hackers the ability to both distribute malware and steal the identity and employment information of candidates for the purposes of forging their identities and impersonating them. I am interested in discussing this topic because I was a victim of such a campaign earlier this year.
I will be discussing the Yahoo data breach, which gaining public attention from articles in 2016. In September 2016, the public was first made aware of a breach at Yahoo that had occurred in late 2014, compromising around 500 million user accounts. This incident was initially considered one of the largest data breaches. However, a few months later, in December 2016, investigations revealed an even larger breach that took place in 2013. This newly disclosed breach affected all 3 billion Yahoo user accounts. This disclosure highlighted the massive scale of cybersecurity issues Yahoo faced and raised concerns about the delay in detecting the breaches and informing the public.
In October 2023, watering hole attacks and social engineering have been utilized to deliver custom IMAPLoader malware onto targeted devices in attacks against the transportation, logistics, and technology sectors of Middle Eastern countries, including Israel. Imperial Kitten, attributed by CrowdStrike, have been active since 2017 but this attacks amid a surge of cyber activity from the Iranian space since the onset of the recent Hamas-Israeli war. The news of this attack came mid-to-late October.
I would like to discuss a new threat/attack made by North Korean threat actor Diamond Sleet (formerly ZINC) involving a malicious variant of a CyberLink Corp. multimedia software product. The malicious file is a legitimate CyberLink application installer that has been modified by the Korean bad actors to include malicious code that downloads, decrypts, and loads a second-stage payload. This file is issued by Cyberlink and is signed using a legitimate certificate and hosted on legitimate update infrastructure owned by CyberLink. This threat is a smart one which makes sure that the device to be infected has no security protection (Vulnerable), otherwise it will not install, and if it installs, the time window for its execution is very limited. The malicious activity has impacted devices in multiple countries, like Canada, USA, Japan, Taiwan, and the United States. This threat was uncovered by Microsoft Threat Intelligence on November 22nd, this year. Microsoft acted on it immediately by informing Cyberlink, GitHub, and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint customers. Afterwards it was public and spread in the news.
ChatGPT's data breach happened during a nine-hour window on March 20 between 1 a.m. and 10 a.m. Pacific time. According to OpenAI. Approximately 1.2% of the active ChatGPT Plus subscribers had their data exposed during this time. During this time, some users could see another user's first and last name, email address, payment address, credit card type, credit card number (the last four digits only), and the credit card expiration date. It was also possible for some users to see the first message of other users' newly created conversations. The breach was caused by a vulnerability in one of its third-party software dependencies, Redis, that made an error where if you canceled a request within a particular timeframe, the system would get confused and decide to deliver your information to the following user who made a similar request because it did not know what to do with it. In response to the incident, Redis' open-source maintainers have addressed the bug and rolled out a patch. Also, ChatGPT OpenAI said they have increased the "robustness and scale" of their Redis cluster to reduce the chance of errors at extreme load.
INSIDERS ARE THE BIGGEST THREATS TO U.S. NATIONAL SECURITY & CRITICAL NATIONAL INFRASTRUCTURE (CNI) According to a May 15, 2023 CIO Influence article, over 77% of organizations in the U.S. critical national infrastructure (CNI) have experienced an increase in insider-driven cyber threats over the past three years, as reported by cybersecurity firm Bridewell. These insider threats range from criminal intent to individual negligence, with intentional acts of destruction occurring bi-weekly on average. The recent Pentagon data leak, involving a junior employee, emphasizes the importance of robust insider threat controls. Bridewell's research, surveying 525 cyber security decision-makers across various sectors, suggests that increased insider threats may be linked to geopolitical tensions and economic pressures. Notably, 35% of CNI organizations reported a rise in employees turning to cybercrime due to poor economic conditions. The research also indicates a high concern for cyberwarfare, with 81% of CNI organizations worried about threats to essential U.S. services. Additionally, the finance sector is particularly vulnerable to ransomware attacks and social engineering, exacerbated by economic uncertainty. Bridewell's Co-CEO Scott Nicholson highlights the need for proactive measures like regular background checks, monitoring, access controls, and continuous cybersecurity education to mitigate insider risks. Bridewell, a global provider of managed detection and response services and cybersecurity consultancy, emphasizes collaboration between private and public sectors to protect national security and recommends organizations take steps to reduce insider risks in the ever-evolving threat landscape. Simultaneously, the U.S. intelligence community faces ongoing challenges in preventing top-secret document leaks, as seen in the case of Jack Teixeira reported on April 13, 2023 and similar instances involving Chelsea Manning, Edward Snowden, and Reality Winner. The difficulty in preventing such leaks is attributed to the vast number of individuals with top-secret clearances and post-9/11 reforms promoting extensive information sharing within the government. Efforts to bolster security and implement "Insider Threat" programs have not fully controlled sensitive data access. The typical profile of leakers includes low-level personnel with access to highly classified information, driven by various motives, from political protest to seeking validation in online communities. This issue is further complicated by the challenge of monitoring the online activities of young military members who might misuse classified information access. Teixeira's case, while addressing immediate leak concerns, underscores the larger, ongoing challenge of securing classified information in the U.S. military and intelligence sectors. REFERENCES CIO Influence News Desk. (2023, May 15). Insider threats surge across US critical infrastructure as 77% under increasing fire from within. CIO Influence: Amplifying IT Content. https://cioinfluence.com/security/insider-threats-surge-across-us-critical-infrastructure-as-77-under-increasing-fire-from-within/ Hill, M. (2023, May 17). Insider threats surge across US CNI as attackers exploit human factors. CSO Online. https://www.csoonline.com/article/575303/insider-threats-surge-across-us-cni-as-attackers-exploit-human-factors.html Meyer, J., & Brook, T. V. (2023, April 14). Pentagon document leak: Here are the biggest takeaways after U.S. military secrets leaked. USA Today. https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/politics/2023/04/13/dod-leaked-documents-pentagon-military-secrets/11648829002/
I'll cover the MOVEit attacks from the perspective of the overall vulnerability and subsequent exploitations. I intend to explore several case study examples of clients that were compromised in an attempt to highlight the variations of the attacks. The vulnerability in MOVEit software was first disclosed publicly in a May 31, 2023, CVE report. The vendor reported the vulnerability the same day but did not have a complete picture of the depth of the issue until a public statement on June 15, 2023. This statement openly acknowledged that customers were actively exploited; some had already been victims of data exfiltration and exploitation campaigns.
I'd like to discuss The Microsoft Exchange Server Compromise. The Microsoft Exchange Server Compromise was caused by four zero-day vulnerabilities in Microsoft Exchange Server, which were exploited by hackers to gain access to user emails and passwords on affected servers. The vulnerabilities were initially launched by the Hafnium hacking group and were patched in March 2023
I would like to discuss the recent ransomware attack that took place at the MGM hotel and Casions on September 10th. In particular, I would like to discuss how the Ransom ware attack took place, and what steps can be taken to prevent a similar attack from occurring in the future.
I would like to discuss the Breach that occurred to U.S. Agencies via Microsoft Cloud services. On July 11, Microsoft publicly disclosed that a group of Chinese hackers spied on U.S. government agencies through vulnerabilities in Microsoft’s cloud services. The attack was first detected in June, and made public in July of 2023. The hacking group was deemed "Storm-0558" by Microsoft.
A May 2023 article on the Hacker News discussed an attack by Mustang Panda, an alleged Chinese state actor, that implanted firmware on the TP-Link routers of several European foreign affairs offices. I found the attack to be instructive based on several different lessons we discussed during the course: the use of firmware to control a device's hardware; how the hackers potentially used brute force to exploit router passwords; how the attack was able to spread across networks; and how the attacks were able to create a mesh network of routers that operated like a TOR network, making detection and recovery especially difficult.
In early October 2023, cyber criminals were able to gain unauthorized access to the "DNA Relatives" feature on the 23andme platform. On October 2023, 23andme representatives confirmed the attack by announcing that hackers obtained some user data. The leaked data included genetic data, personal identifiers, full names, usernames, profile photos, sex, date of birth, geographical locations, and genetic ancestry results. It has been confirmed that a cybercriminal known as Golem leaked these records (approximately 4 million users) on a forum. It has not been confirmed what specific resource was compromised (i.e. web server, database, etc) but considering the nature of the information obtained, presumably a database was compromised via access from a web server.
I would like to summarize the zero-day vulnerability that affected the MoveIT Transfer software in May/June 2023 impacted organizations across the world. The vulnerability was announced publicly, by the vendor, on May 31st, 2023 causing all users of it's software to incident their incident response protocols.
I would like to discuss a cybersecurity concern that arose from the recent compromise of Okta's support system. In October 2023, Okta, a major identity and access management service provider, revealed that hackers had gained access to its support case management system using a stolen credential. This event affected approximately 18,000 companies, and the data of all of Okta's clients was compromised. The stolen data included names, email addresses, and in some cases, other personal information. This hack highlights the importance of ensuring credential security and the potential for a single cybersecurity event to have far-reaching consequences.
The introduction of the .zip and .mov top-level domains (TLDs) in 2022 has raised concerns about potential security risks and usability issues. These TLDs, which correspond to common file formats among many (such as .dad, .phd, .prof, .esq, .foo etc), could be misused for phishing attacks or accidentally triggered by software that automatically converts text into links. Google introduced these in May, 2023, and received a major criticism. Researchers References: "8 new top-level domains for dads, grads and techies" by Google - https://blog.google/products/registry/8-new-top-level-domains-for-dads-grads-tech/
In my final project, I will be discussing the F5 BIG-IP SQL Injection vulnerability, or CVE-2023-46747. Since the attack unfolded just weeks ago on or around 10/26, the vulnerability has expanded to a larger advisory containing many other CVEs impacting the F5 product line. To summarize, CVE-2023-46747 allows unauthenticated users to bypass Configuration utility authentication and CVE-2023-46748 allows an authenticated attacker with access to the Configuration utility to perform a SQL injection. The vulnerability allowed attackers to carry out AJP (Apache Jserv Protocol) request smuggling. To capitalize on this flaw, a message with a mandatory POST body length of 0x204 was submitted and the AJP listener would interpret it as an AJP POST request and send it wherever the attacker wanted. After further research conducted by the company, it was found that a smuggled AJP packet with arbitrary content could create administrator credentials and run arbitrary commands through the ‘mgmt’ API. Though subject to change, I intend to structure the final project as follows: 1. Introduction: - Provide overview of the project's objectives and describe the F5 BIG-IP vulnerability 2. Background and Context: - Provide background information on the attack, including historical context/impact - Discuss attacker motivations and techniques in SQL injection attacks - Describe potential consequences and risks associated with SQL injection attacks 3. Attack Analysis: - Analysis of attack including its methodology, attack vectors, and vulnerabilities exploited - Tools, techniques, and tactics used by adversaries in this type of attack - Include case studies of potential impact on organizations 4. Prevention and Mitigation: - Recommendations and best practices in SQL injection prevention and mitigation - Discuss network security, access controls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems - Address organizational change management aspects associated with recovery 5. Implementation and Testing: - Outline recommended best practice guidelines - Challenges and considerations involved in implementation 6. Conclusion: - Summarize key findings 7. References
I'd like to discuss the security breach that happened to Casio, the Japanese electronics producer. This attack happened on October 11th where an unauthorized attacker accessed a database for "classpad.net" resulting in personal information leaks of customers both in and out of Japan.
I want to discuss the MGM Casino data breach and ransomware incident that occurred last September. According to the reports, the attackers gained access to the target network on September 8th. The incident was made public on September 11th. Scattered Spider, an APT group, was behind the attack. They accessed the networks using social engineering methods and employed ransomware developed by the ALPHV ransomware group. The incident involved privilege escalation and lateral movement activities. The attackers requested a $30 million ransom payment; however, MGM refused to pay the ransom. The company lost around $100 million dollars.
A worm named LitterDrifter was used by Russian cyber espionage actors (they have a link to the Federal Security Service) against Ukrainian entities in November 2023 (Made public in November 2023). LitterDrifter is a worm that spreads through a hidden file in a USB drive and uses command and control (C&C) servers to spread. Like a previous famous worm, Stuxnet, LitterDrifter uses a spreading module to create hidden files and decoy shortcuts on USBs. Note it is written in VBS (Visual Basic Scripting). Check Point (Cybersecurity solutions company) mentions its functionality is simple yet effective. Gamaredon (known for large-scale data collection campaigns) is a Russian-state hacker group that mainly motivated these activities. These activities likely extend beyond Ukraine to other countries, such as the US.
I would like to discuss the 23andMe hacking incident. This occurred around August-October of 2023. An adversary was able to gain access to 23andMe user data by using credential stuffing. The adversary was also able to gain access to user data for any accounts that were connected to those that they gained access to through the credential stuffing as well.
I will be covering the MOVEit hack carried out against PBI Research Services In May 2023 and was made public in July 2023. PBI Research provides population, death, and location services to large pension and insurance firms. The May 2023 attack impacted about 5 million individuals including members of the California Employee's Retirement System. MOVEit is a managed file transfer software product that encrypts files and uses file transfer protocols such as FTP(S) or SFTP to transfer data. The data breach occurred when a SQL injection vulnerability in MOVEit Transfer and MOVEit Cloud (CVE-2023-34362) was exploited. The vulnerability allowed an attacker to access MOVEit Transfer’s database from its web application without authenticating. The attacker could then execute SQL statements that alter or delete entries in the database, and infer information about the structure and contents of the database.
CVE-2023-36934 is a security vulnerability identified in several versions of the MOVEit Transfer web application. This vulnerability is a SQL injection flaw, which could allow an unauthenticated attacker to gain unauthorized access to the MOVEit Transfer database. By submitting a specially crafted payload to a MOVEit Transfer application endpoint, an attacker could potentially modify and disclose content from the MOVEit database. This issue was disclosed as a zero day vulnerability in May 2023 and allowed ransomware and extortion gangs to raid servers using the MOVEit protococol to breach and steal sensitive data for ransom payments. The estimated fallout of the hacks is estimated at over $9 billion dollars.
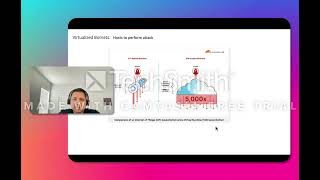
In August/ September 2023, a Zero-day vulnerability in HTTP/2 protocol was exploited to launch largest DDoS attack by using botnets. The technique is called "HTTP/2 Rapid Reset". Cloudflare, Google and AWS all successfully mitigate this attack. Cloudfare said the attack peaked at 201 million RPS, Google recorded 398 million RPS
"MGM Resorts operations halted by cyber attack". First discovered on September 11, 2023. This is multifaceted as many systems appear to have been compromised. It didn't just steal data, it affected systems in the casinos. This one is very personal for me as well as being topical. My company provides high speed internet to their aircraft fleet. Afterwards, I had to fly in personally to meet with the flight department and discuss options to bolster their cyber posture as it applied to the aircraft even though the breach was independent of this attack.
The threat that I would like to discuss is the MoveIT Hack-Transfer vulnerability performed by the CL0P Ransomware Gang. The vulnerability was marked as Zero Day vulnerability on May 31, 2023, and on June 15, 2023, it was classified under MOVEit Transfer Critical Vulnerability – CVE-2023-35708. The threat actor and hack contain several topics reviewed in class. Also, it provides visibility on how companies and government agencies reacted to stop the threat and provide public knowledge and visibility on the attack. The hack was performed by a SQL injection vulnerability found on the MOVEit software used by many organizations. It executed statements that allowed database changes and provided the threat actor with a tool to exfiltrate information to continue attacks in several other organizations.
I would like to discuss the MOVEIt data breach that occurred in May 2023. It was a zero-day exploit in a managed file transfer service used by a large number of organizations around the world and allowed attackers to gain access to sensitive customer data. This affected both my personal and professional lives as one of my private accounts was using MOVEIt and my company also utilized it for transferring files to and from customers.
Joshua Anthony Marquis Covington
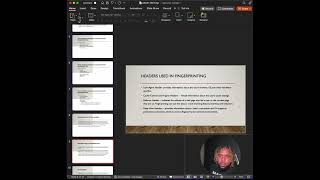
Fingerprinting is a double-edged sword and while it can have a beneficial use case such as fraud detection, it poses significant privacy concerns that can be exploited for tracking/profiling users without them knowing. GitGuardian's engineers worked on a solution to scan and ensure developers aren't pushing their secrets to their repositories for others to see. In order to do this a secret fingerprinting tool, which allows security practitioners to be proactive in seeing secrets were leaked, was developed. In 2022 GitGuardian found over ten million public commits that had secrets present.
I would like to discuss the MOVEit vulnerability exploited by CLOP earlier this year. It was discovered and patched on May31st, but many companies were breached during the time before it was patched.
For the final project, I plan to present on the rising threat of ransomware, particularly a newer strain of ransomware known as "3AM." This ransomware strain was first reported on in September 2023 by Symantec, and so far it has only been found in one attack. 3AM is written in Rust, and it influences many parts of an infected system by stopping processes, escalating privilege, and exfiltrating target data. It is also able to stop various security protocols on a device. When 3AM was discovered, it was used as an alternative after LockBit failed to infect a system. Though the origins of this ransomware are still unknown, understanding how the malware works is crucial to protecting against it.
John Hopkins University and Health System being target of a cyber attack is what I will be discussing. It happened on May /31/2023. Due to vulnerabilities in a software that were exploited, resulting into data breaches of John Hopkins University and its hospital plus also other major large companies which used this same software.Later John Hopkins informed all its employees ,students ,patients about this breach so as to take the necessary steps to protect them selves(personal information).The Software involved was called MOVEit. Information about this attack was made public on June/14/2023
Klever Wallet Vulnerability: The threat under consideration stems from a known exploit related to low-entropy mnemonics, impacting the Klever crypto wallet that exhibited suspicious activity on July 12th, 2023. This exploit, linked to the Random Generation algorithm used in the Bip39 implementation, was previously flagged by the TrustWallet explorer extension in April 2023. The algorithm, once widely adopted by various cryptocurrency wallet providers, contains a flaw that compromises the security and unpredictability of generated keys. This vulnerability raises concerns about potential unauthorized access or malicious activities targeting affected wallets.
For the final project, the threat I would like to discuss is the high-profile cyberattack that incurred approximately $100 million in damages for MGM Resorts (and I must confess I did not select this topic based on the example given by the teaching fellow in the Ed tool, I always wanted to research on this particular attack and this final project assignment was the perfect avenue). The cybersecurity incident came to light on September 12, 2023, when MGM Resorts International issued a statement revealing the identification of a cyber threat impacting their systems. Notably, the Company officially reported the incident to the UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION on October 5, 2023, with detailed information available in the filing accessible at "https://www.sec.gov/ix?doc=/Archives/edgar/data/789570/000119312523251667/d461062d8k.htm." In a proactive measure to contain the potential harm to customer information, MGM Resorts intentionally initiated a shutdown of various services. The repercussions were profound, causing significant disruptions to MGM's operations. Key cards for hotel customers became non-functional, corporate emails were inaccessible for employees over several days, and diverse systems such as slot machines, electronic payments, digital keycards, ATMs, and paid parking experienced disruptions. Remarkably, reports suggest that the cyberattack was executed in a remarkably brief span of approximately ten minutes. During the incident, MGM CEO Bill Hornbuckle publicly acknowledged that the hackers had successfully accessed and pilfered certain customers' personal information. This compromised data included sensitive details such as names, driver's license numbers, and Social Security numbers, constituting a serious breach of privacy and security.
I'd like to discuss the ChatGPT data leak in March 2023, where over a 9-hour window some users were able to see titles from another user’s chat history. This was due to a bug where in one of ChatGPT's dependencies (an open-source library), which allowed for corrupted connections (returning responses from one user's requests to another user). Open AI has since patched up this bug and launched a bug bounty program.